Neptune
Neptune, the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun, holds an air of mystery and allure in our solar system. Named after the Roman god of the sea, Neptune's deep blue hue and captivating features evoke a sense of cosmic wonder. As a gas giant, it is the fourth largest planet, boasting a diameter approximately four times that of Earth. Neptune is located over 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) away from the Sun, which contributes to its frigid temperatures and inhospitable conditions.
Introduction to neptune
Neptune, the eighth and farthest known planet from the Sun, holds an air of mystery and allure in our solar system. Named after the Roman god of the sea, Neptune's deep blue hue and captivating features evoke a sense of cosmic wonder. As a gas giant, it is the fourth largest planet, boasting a diameter approximately four times that of Earth. Neptune is located over 4.5 billion kilometers (2.8 billion miles) away from the Sun, which contributes to its frigid temperatures and inhospitable conditions. With its turbulent atmosphere, intriguing rings, and enigmatic moons, Neptune beckons scientific exploration to unravel its secrets and shed light on the dynamics of the outer reaches of our celestial neighborhood. Its study not only enhances our understanding of Neptune itself but also offers valuable insights into the formation, evolution, and diversity of planets throughout the universe

The composition and structure of Neptune
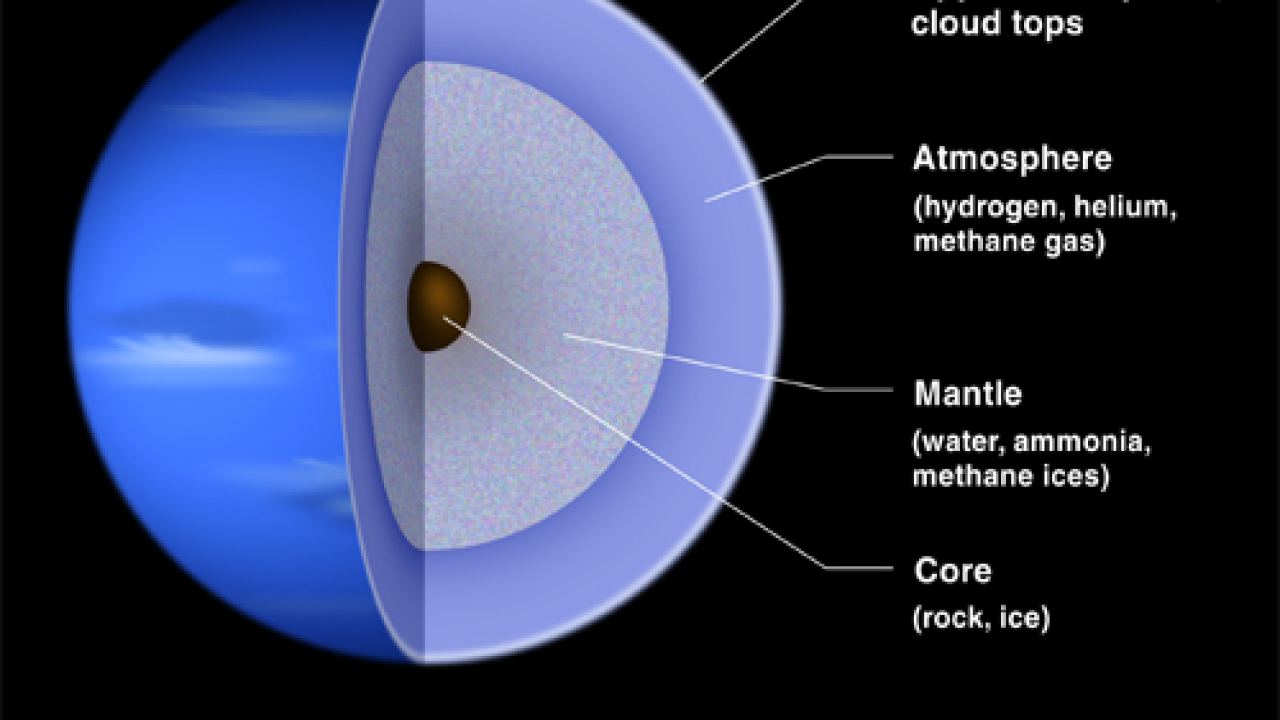
The composition and structure of Neptune, the distant ice giant, offer a glimpse into the complex nature of this enigmatic planet. Neptune is primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, similar to its gas giant counterpart, Jupiter. However, its composition also includes a significant amount of ices, such as water, methane, and ammonia, which give Neptune its striking blue coloration. These ices, along with trace amounts of hydrocarbons and other compounds, contribute to the unique chemistry of Neptune's atmosphere. Beneath its gaseous envelope, Neptune is believed to possess a solid core made up of rock and metal. This core is estimated to be about the size of Earth and is surrounded by a mantle consisting of water, ammonia, and methane ices. The mantle extends upward, transitioning into the planet's atmosphere, where it interacts with the outer environment.

The exploration of Neptune
The exploration of Neptune, one of the most distant and elusive planets in our solar system, has been a limited yet significant endeavor. The Voyager 2 spacecraft remains the only mission to have visited Neptune, completing a flyby in 1989. Voyager 2 captured stunning images of the planet's vibrant atmosphere, revealing intricate cloud patterns, massive storms, and even a mysterious dark spot dubbed "The Great Dark Spot." During its encounter, Voyager 2 also discovered and studied Neptune's system of moons, including Triton, the largest moon of the planet. Triton's peculiar backward orbit and unique surface features sparked scientific interest and provided insights into the moon's formation and evolution.e